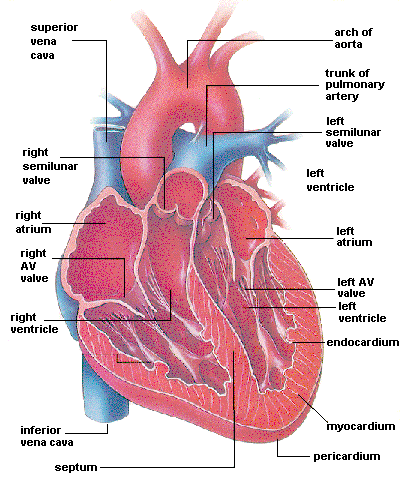
Aorta – The aorta carries oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the body, dividing into smaller arteries. The thoracic aorta (including the ascending aorta; aorta arch and descending aorta) supplies the upper body. The abdominal aorta supplies the lower body.
Arrhythmia – An irregular heartbeat resulting from any change, deviation or malfunction in the heart’s electrical system. An arrhythmia may be abnormally fast (tachycardia) or abnormally slow (bradycardia) and some can be fatal (e.g. ventricular fibrillation).
Atrial Fibrillation – A rapid, irregular heart rhythm caused by abnormal electrical impulses that begin in the upper chambers of the heart (atria). As a result, the heart’s lower chambers (the ventricles) beat rapidly and irregularly.
Bradycardia – An abnormally slow heart beat (less than 60 beats per minute).
Bundle Branch Block – Is a condition in which the electrical impulses traveling through the heart are slowed or blocked completely from traveling along their normal route through the ventricles.
Heart Block – The delayed or complete lack of electrical communication between the heart’s upper chambers (atria) and lower chambers (ventricles). This causes abnormally slow heart rhythms known as bradycardias.
Inappropriate Sinus Tachycardia – A rare and usually harmless condition in which the heart is normal but the heart rate is unusually fast, both at rest and in response to physical activity. Its cause is unknown and the condition could lead to fainting or fatigue.
Long QT Syndrome – Long QT Syndrome (LQTS) is a rare, usually inherited and sometimes fatal disorder of the heart’s electrical system. It may lead to a rapid heartbeat in those of stress, fear or anger and can cause fainting or even cardiac arrest.
Premature Ventricular Contractions – An irregular heartbeat that occurs when the heart’s lower chamber (ventricles) are told to pump too soon but a signal that came from an area other than the sinus node (the heart’s natural pacemaker). This could happen once or several times in a row.
Sick Sinus Syndrome – A condition in which the sinus node (the heart’s natural pacemaker) malfunctions, causing an irregular heart rhythm.
Strokes Adams Disease – An interruption in the path of electrical impulses from the atria to the ventricles, creating a lack of communication regarding the heartbeat (a heart block). Causes an abnormally slow heartbeat and even fainting from lack of oxygen to the brain.
Wolf Parkinson White Syndrome – Malformed electrical pathways between the heart’s chambers cause signals to arrive too soon and too fast to the ventricles and then "bounce back" to the ventricles prompting a rapid and irregular heart beat.